Academic Background
Silvia Corvera is Professor of Molecular Medicine, director of the MD/PhD (MSTP) program, and director of the Clinical Translational Research Pathway. She holds the Endowed Chair in Diabetes Research.
She received her M.D. and MSc in Molecular Biology at the Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico, and was awarded a Fogarty International Fellowship to conduct postdoctoral studies in the US. She was on the Faculty at the Department of Pathology at the University of Pennsylvania (1987-1990) before moving to the newly formed Program in Molecular Medicine at the University of Massachusetts Medical School.
Current Research
Metabolic diseases, such as type-2 diabetes, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NASH), and hypertension are an emerging worldwide epidemic associated with substantial human suffering and a large economic burden. We are interested in understanding the cellular and molecular mechanisms that underlie metabolic diseases, and enable therapeutic strategies to be developed.
We are specifically interested in human adipose tissue. Adipose tissue has amazing properties: each adipocyte can expand its size very rapidly, and is able to increase lipid storage 4-5 fold. In response to fasting, it rapidly releases this lipid to provide energy to the entire body. However, there seems to be a maximal capacity to expand, and when this capacity is reached adipocyte function fails. How the adipocyte can change its volume so dynamically is a very interesting cell biology question, and a very relevant one in understanding metabolic disease mechanisms. In fact, at similar weight, individuals whose adipose tissue is made up of many small adipocytes are at a lower risk of metabolic disease compared to individuals whose tissue contains fewer large adipocytes. Thus, one of our main interests is to understand the mechanisms that control the number and size of adipocytes.
Another amazing property of adipose tissue is its diversity of functions. We usually think of adipose tissue as a site for fat storage. However, a form of adipose tissue, called “brite” or “beige” in humans, is constantly burning fat to generate heat. “Brite/beige” adipose tissue is localized around the neck, close to major blood vessels, where the heat generated can serve to maintain core temperature. Humans who have more of this heat-generating adipose tissue tend to be lean and metabolically healthy, but what mechanisms underlie this correlation is not known. We have developed an approach to generate human “brite/beige” adipocytes in-vitro, and found that these cells can improve glucose metabolism when implanted into immune-compromised mice. A major goal now is to understand the mechanism for this effect, by discovering what factors stimulate the proliferation and differentiation of human brite/beige adipocytes, and whether these cells improve glucose metabolism through consumption of energy, through effects on other tissues, or both.
Another great unknown in the field of adipose tissue are the genetic factors that define its body pattern. Some individuals develop more adipose tissue under the skin in upper or lower extremities, while others have larger amounts in the abdominal region. These latter individuals are at a much higher risk of metabolic disease, even with little weight gain. We have developed an approach to generate adipose tissue “organoids”, starting from minute fragments of human adipose tissue that can be obtained through needle suction. These fragments can be induced to develop microvasculature and new adipocyte progenitors, which differentiate into functional adipocytes within a multicellular context. By studying the properties of adipose organoids generated from different body sites, and from individuals with differing body shapes, we hope to gain insight on the major determinants of human adipose tissue patterning.
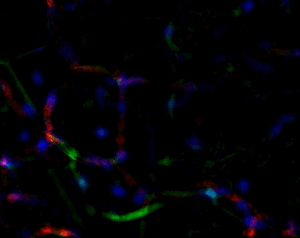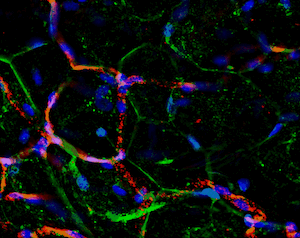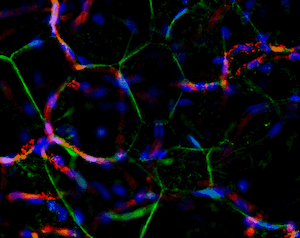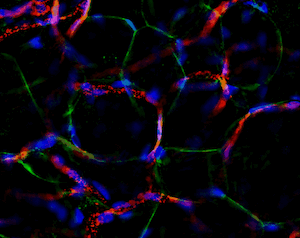

Strong collaborations with clinical partners from the Departments of Surgery and OBGyN have allowed us to use human adipose tissue for our studies and determine how these are associated with diseases such as type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes.